Recently, the Key Laboratory of Coal Environment-Related Diseases and Prevention of the Ministry of Education at our university published a high-level paper titled "Genetic evidence for the causal relations between metabolic syndrome and psychiatric disorders: a Mendelian randomization study" in the top-tier journal Translational Psychiatry, which belongs to the first quartile of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Associate Professor Gao Xue from the Department of Biostatistics at the School of Public Health was the first author, while Professor Wang Tong was the corresponding author.
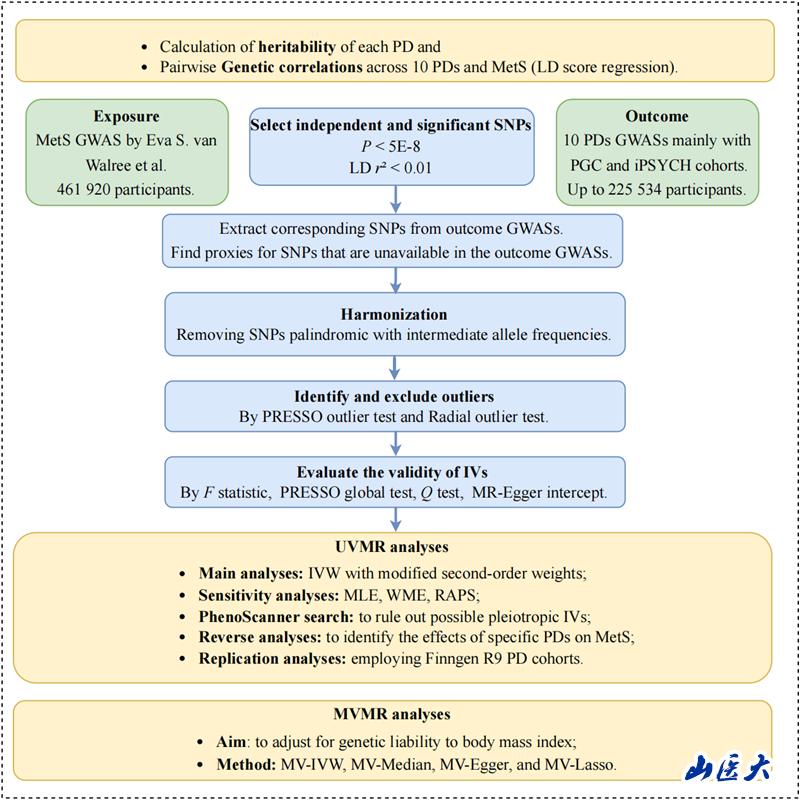
Psychiatric disorders (PDs) are prevalent worldwide, and according to the World Health Organization, hundreds of millions of people worldwide are affected by PDs. With changes in lifestyle and the influence of social and work environments, the incidence of PDs is on the rise, causing significant health and economic burdens to patients and society. The etiology of PDs is complex, and extensive evidence suggests that metabolic syndrome (MetS) is associated with an increased risk of PDs. However, there is no conclusive evidence regarding the causal relationship between MetS and PDs. In this study, based on publicly available genome-wide association analysis databases, the authors used the linkage disequilibrium score regression (LDSC) and Mendelian randomization (MR) models to evaluate the causal relationship between MetS and ten major PDs, as shown in Figure 1. The main results of the study showed that MetS is causally related to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), major depressive disorder (MDD), and anorexia nervosa (ANO). This finding clarifies the causal relationship between MetS and the three PDs mentioned above and contributes to a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of PDs, providing theoretical evidence for the development of public health intervention programs.
The research team conducted theoretical research related to the Mendelian randomization model and its application in pathogenic analysis, with the support of two National Natural Science Foundation grants. They published "Statistical Consensus on the Mendelian Randomization Model and its Standardized Application" on behalf of the Chinese Clinical Oncology Society's Biostatistics Expert Committee's Real-World Research Working Group, providing guidance and suggestions for the correct application of MR in pathogenic analysis. In terms of the pathogenesis of PDs, the team revealed the causal relationships between factors such as sleep status, physical activity, and various PDs, providing many meaningful clues to improve the complex pathogenic network of PDs. The results were published in international authoritative journals in the field of psychiatry and psychology, such as European Psychiatry and Journal of Affective Disorders, with the latter selected by the journal as an editor's recommended highlight article.